| Eta/Pi0 ratio inside jets as function of pT for different jet pT intervals
|
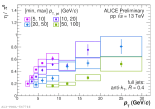
|
| Ratio of fully corrected Eta pT spectra inside jets (data and PYTHIA) to parameterization
|
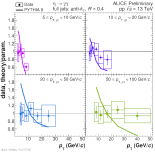
|
| Eta pT spectra in different jet pT intervals normalized per jet
|
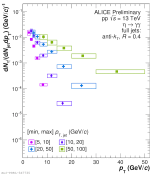
|
| Ratio of fully corrected Pi0 pT spectra inside jets (data and PYTHIA) to parameterization
|
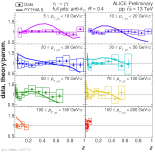
|
| Pi0 pT spectra in different jet pT intervals normalized per jet
|
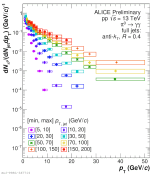
|
| Ratio of Eta pT spectra in different jet pT intervals to a fit to the inclusive Eta spectrum
|
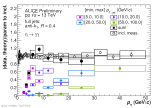
|
| Eta pT spectra in different jet pT intervals normalized per event
|
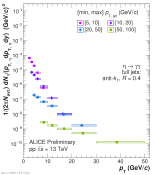
|
| Ratio of Pi0 pT spectra in different jet pT intervals to a fit to the inclusive Pi0 spectrum
|
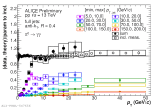
|
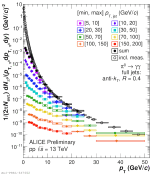
| Pi0 pT spectra in different jet pT intervals normalized per event and the inclusive Pi0 spectrum
|
|
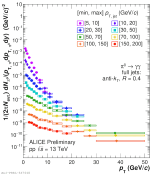
| Pi0 pT spectra in different jet pT intervals normalized per event
|
|
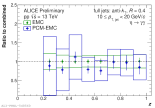
| Comparison of corrected Eta spectra inside jets from different reconstruction methods as function of z
|
|
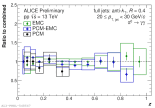
| Comparison of corrected Pi0 spectra inside jets from different reconstruction methods as function of z
|
|
| Comparison of $\lambda_{\theta}$ with UPC measurement
|
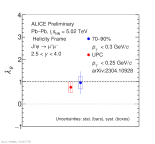
|
| dNdcostheta vs costheta in Pb--Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV using Helicity Frame
|
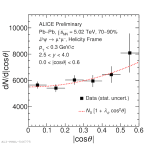
|
| Invariant mass distribution of dimuon pairs for 0.5 < |cos\theta| < 0.6 in Pb-Pb collsions at 5.02 TeV
|
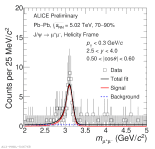
|
| Invariant mass distribution of dimuon pairs for 0.2 < |cos\theta| < 0.3 in Pb-Pb collsions at 5.02 TeV
|
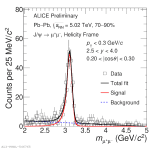
|
| Invariant mass distribution of dimuon pairs for 0.0 < |cos\theta| < 0.1 in Pb-Pb collsions at 5.02 TeV
|
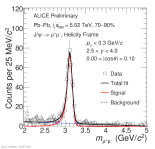
|
| y-differential upsilon(1S) and upsilon(2S) pp cross section at 13 TeV compared to ICEM+FONLL
|

|
| pT differential Upsilon(1S) and upsilon(2S) cross section in pp collisions at 13 TeV compared to ICEM+FONLL
|
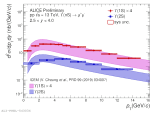
|
| Integrated Upsilon(1S) and Upsilon(2S) cross section as a function of energy compared to ICEM+FONLL model calculations
|
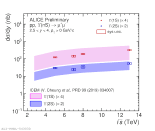
|
| pT differential Upsilon(1S) and upsilon(2S) cross section in pp collisions at 13 TeV compared to LHCb
|
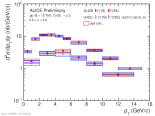
|
| y-differential upsilon(1S) pp cross section at 13 TeV compared to lower energy ALICE data
|
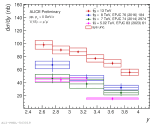
|
| y-differential upsilon(1S) and upsilon(2S) pp cross section at 13 TeV compared to LHCb
|
|
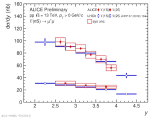
| y-differential upsilon(1S) and upsilon(2S) pp cross section at 13 TeV
|
|
| pT differential Upsilon(1S) and Upsilon(2S) cross section in pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
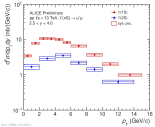
|
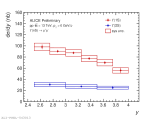
| pT differential Upsilon(1S) cross section in pp collisions at 13 TeV compared to lower energy ALICE data
|
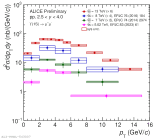
|
| D0-tagged jets compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 on left and to their ratio on right for $\alpha=3$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
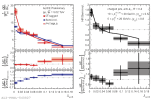
|
| D0-tagged jets compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 on left and to their ratio on right for $\alpha=2$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
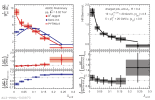
|
| D0-tagged jets compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 on left and to their ratio on right for $\alpha=1.5$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
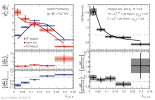
|
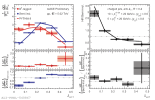
| D0-tagged jets compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 on left and to their ratio on right for $\alpha=1$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
|
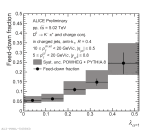
| Feed-down fraction in D$^{0}$-tagged jet angularity in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c and 5 < $p_{\rm T,D^{0}}$ < 20 GeV/c for R = 0.4, $\alpha=1$.
|
|
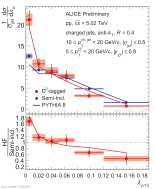
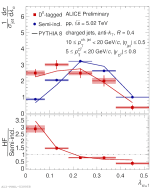
| Fully corrected jet angularity distributions of D0-tagged jet compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 for $\alpha=3$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
|
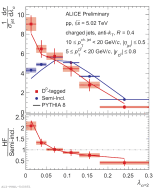
| Fully corrected jet angularity distributions of D0-tagged jet compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 for $\alpha=2$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
|
| Fully corrected jet angularity distributions of D0-tagged jet compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 for $\alpha=1.5$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
|
| D0-tagged jet raw angularity distributions for $\alpha=1$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c and 8 < $p_{\rm T,D^{0}}$ < 12 GeV/c.
|
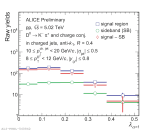
|
| Invariant mass distribution of D$^{0}$-tagged jet candidates with 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c and 8 < $p_{\rm T,D^{0}}$ < 12 GeV/c for R = 0.4.
|

|
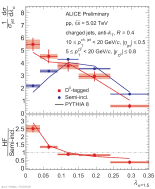
| Fully corrected jet angularity distributions of D0-tagged jet compared to semi-inclusive jets and to PYTHIA 8 for $\alpha=1$, $R=0.4$ in 10 < $p_{\rm T, ch. jet}$ < 20 GeV/c.
|
|
| Response matrix for R=0.3 jets in central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
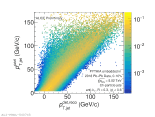
|
| Corrected jet $p_{T,jet}$ distribution with $p_{T}^{lead} > 5$ GeV/c for central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
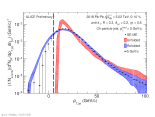
|
| Raw correlated inclusive jet $p_{T,jet}^{reco}$ distribution for central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
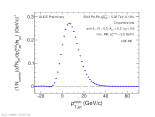
|
| Raw correlated quasi-inclusive jet $p_{T,jet}^{reco}$ distribution with $p_{T}^{lead} > 5$ GeV/c for central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
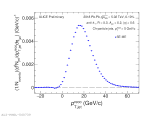
|
| Raw inclusive jet $p_{T,jet}^{reco}$ distribution of the SE and ME for central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
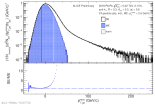
|
| Raw quasi-inclusive jet $p_{T,jet}^{reco}$ distribution of the SE and ME with $p_{T}^{lead} > 5$ GeV/c for central Pb-Pb collisions at 5.02 TeV
|
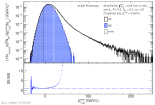
|
| Invariant Cross-Section Ratios of Different Jet Radii for pp Full Jet Spectra 8 TeV with Comparison to PYTHIA8
|
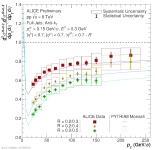
|
| Fragmentation function of J/psi-tagged charged jets
|
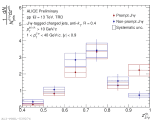
|
| Fragmentation function of non-prompt J/psi-tagged charged jets
|
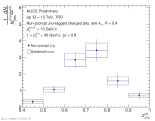
|
| Fragmentation function of prompt J/psi-tagged charged jets
|
|
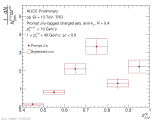
| f_B signal extraction 0.7 < z < 0.8
|
|
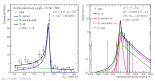
| Inclusive jpsi signal extraction, 0.7 < z < 0.8
|
|
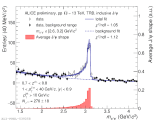
| Fiducial cross section of Z->ee at mirapidity in pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
|
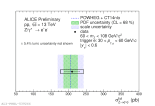
| Invariant mass of Z->ee (ULS and LS pairs) at midrapidity in pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
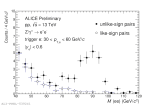
|
| Invariant mass of Z->ee at midrapidity in pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
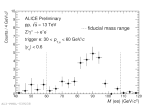
|
| The comparison of longitudinal momentum fraction of $\rm D_{s}^{+}$ and $\rm D^{0}$ -tagged jets in MB pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
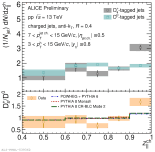
|
| Longitudinal momentum fraction of $\rm D_{s}^{+}$-tagged jets in MB pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
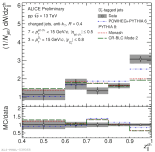
|
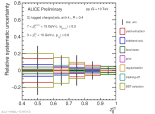
| Relative statistical and systematic uncertainties by categories of $\rm D_{s}^{+}$-tagged jets longitudinal momentum fraction in MB pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
|
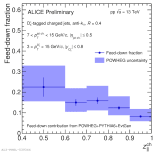
| Feed-down contribution of $\rm D_{s}^{+}$ jets from POWHEG+PYTHIA6+EvtGen in MB pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
|
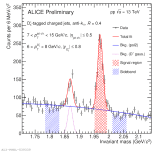
| Invariant mass distribution of $\rm D_{s}^{+}$ candidates inside jets in MB pp collisions at 13 TeV
|
|
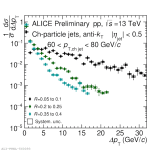
| Energy flow distributions overview Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.05 to 0.1, R=0.2 to 0.25 and R=0.35 to 0.4
|
|
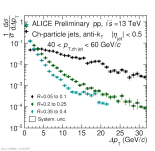
| Energy flow distributions overview Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.05 to 0.1, R=0.2 to 0.25 and R=0.35 to 0.4
|
|
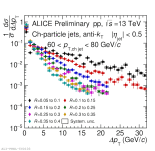
| Energy flow distributions overview Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV, All Rjet pairs
|
|
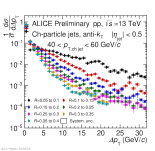
| Energy flow distributions overview Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV, All Rjet pairs
|
|
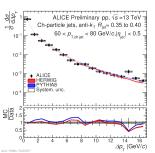
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.35 to R=0.4
|
|
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.35 to R=0.4
|
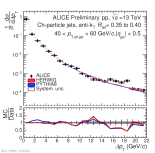
|
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.2 to R=0.25
|
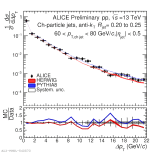
|
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.2 to R=0.25
|

|
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.05 to R=0.1
|
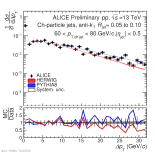
|
| Energy flow distributions with model comparison Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV, R=0.05 to R=0.1
|
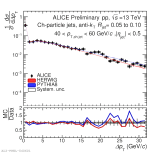
|
| Mean energy flow versus jet radius with model comparison Charged jets 60-80 GeV pp 13 TeV
|
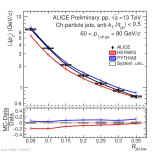
|
| Mean energy flow versus jet radius with model comparison Charged jets 40-60 GeV pp 13 TeV
|
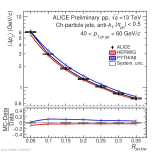
|
| Mean energy flow versus jet radius with jet pt dependence Charged jets pp 13 TeV
|
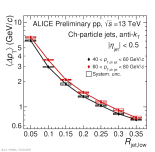
|
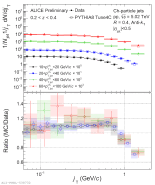
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in high $z$ bin compared to PYTHIA8 Tune4C
|
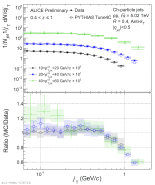
|
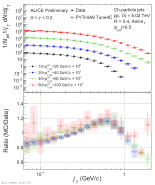
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in mid $z$ bin compared to PYTHIA8 Tune4C
|
|
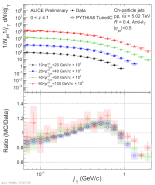
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in low $z$ bin compared to PYTHIA8 Tune4C
|
|
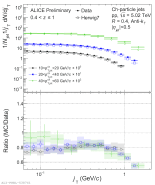
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in inclusive $z$ bin compared to PYTHIA8 Tune4C
|
|
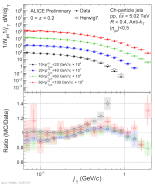
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in high $z$ bin compared to Herwig
|
|
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in mid $z$ bin compared to Herwig
|
|
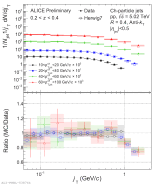
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in low $z$ bin compared to Herwig
|
|
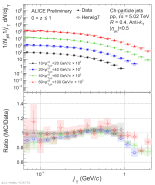
| Measured $j_\mathrm{T}$ distributions in inclusive $z$ bin compared to Herwig
|
|
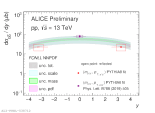
| [HP 2023] Beauty cross section as a function of rapidity compared with FONLL prediction (NNPDF pdf)
|
|
| [HP 2023] Beauty cross section as a function of rapidity compared with FONLL prediction (CTEQ6 pdf)
|
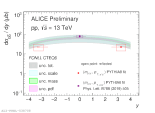
|
| [HP 2023] Charm cross section as a function of rapidity compared with FONLL prediction (CTEQ6 pdf)
|
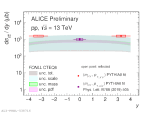
|
| [HP 2023] Charm cross section as a function of rapidity compared with FONLL prediction (NNPDF pdf)
|
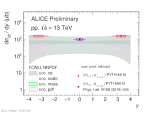
|
| [HP 2023] Simultaneous unbinned fit to dimuon data distribution (transverse momentum component)
|
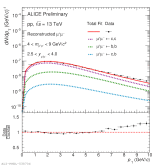
|
| [HP 2023] Simultaneous unbinned fit to dimuon data distribution (mass component)
|
|
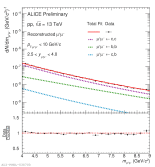
| [HP 2023] Dimuon invariant mass distribution with m>4 Gev/c^2
|
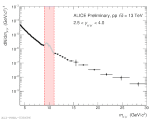
|
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section Ratio for R = 0.2/0.5 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
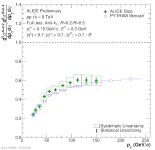
|
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section Ratio for R = 0.2/0.4 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
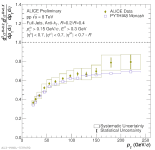
|
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section Ratio for R = 0.2/0.3 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
|
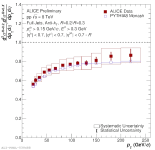
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section for R = 0.5 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
|
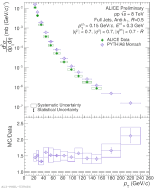
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section for R = 0.4 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
|
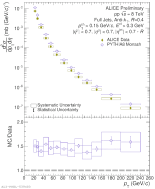
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section for R = 0.3 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
|
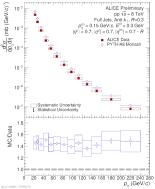
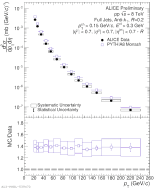
| Comparison of the Invariant Cross-Section for R = 0.2 Full Jets in pp to PYTHIA8 Monash
|
|
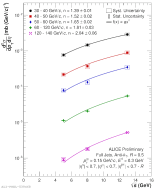
| $\sqrt{s}$ Comparison for Several Bins in $p_{T}^{jet}$ for R = 0.5 - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|
|
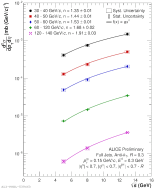
| $\sqrt{s}$ Comparison for Several Bins in $p_{T}^{jet}$ for R = 0.4 - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|

|
| $\sqrt{s}$ Comparison for Several Bins in $p_{T}^{jet}$ for R = 0.3 - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|
|
| $\sqrt{s}$ Comparison for Several Bins in $p_{T}^{jet}$ for R = 0.2 - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|

|
| Compilation of Invariant Cross-Sections for R = 0.5 in pp Full Jet Spectra - 5, 8, 13 TeV
|

|
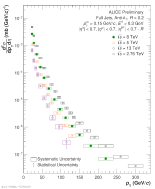
| Compilation of Invariant Cross-Sections for R = 0.4 in pp Full Jet Spectra - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|

|
| Compilation of Invariant Cross-Sections for R = 0.3 in pp Full Jet Spectra - 5, 8, 13 TeV
|
|
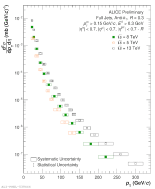
| Compilation of Invariant Cross-Sections for R = 0.2 in pp Full Jet Spectra - 2.76, 5, 8, 13 TeV
|
|